Lice Facts
EVERYTHING YOU’VE EVER WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT HEAD LICE
The American Academy of Pediatrics estimates that 6-12 million people get head lice in the US each year. Contrary to some myths, lice are just as likely to infest a clean head as they are a dirty one. While the thought of bugs in a child’s hair may be upsetting – there’s no reason to panic!

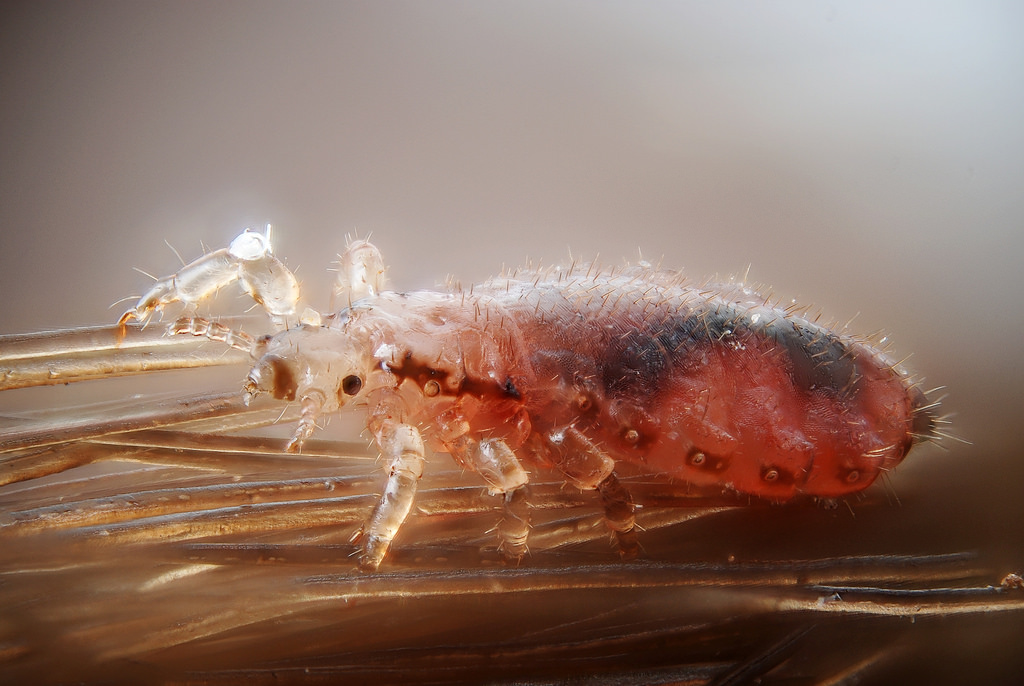
Female human head louse, Pediculus humanus capitis.
Technical settings :
- focus stack of 46 images
- microscope objective (Nikon achromatic 10x 160/0.25) directly on the body (with adapter ~30 mm)
Common Lice Facts at A Glance:
What Are Head Lice?
1. Head lice are tiny wingless insects.
2. They have 6 legs and do NOT fly, jump or hop, but they move very fast.
3. They are human parasites that feed on the blood of the infested person.
4. They obtain the blood through a person’s scalp, which is what makes them itch.
How Prevent the Spread of Head Lice:
1. The main way lice are spread is head-to-head contact.
2. Do not share hair-related personal items.
3. Avoid sleepovers and slumber parties during lice outbreaks
4. Machine wash and dry, at high temperatures, any bedding and clothing used by anyone having lice.
5. Call us for Lice Removal in Southern California
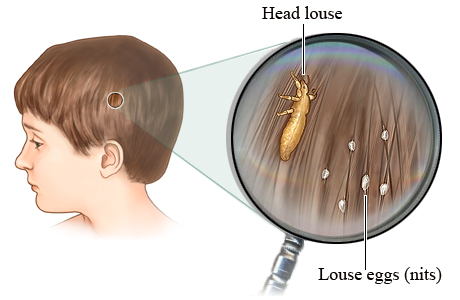
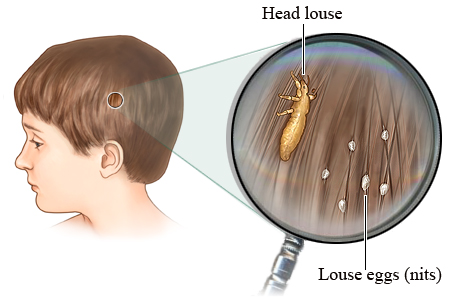
How Big are Lice and Their Eggs?
1. Nits (or eggs) are about the size of the letter “O” on the back of a penny
2. Nits are attached to the hair with a strong glue-like substance
3. Adult lice are about the size of a sesame seed or the size of the word “ONE” on the back of a penny.
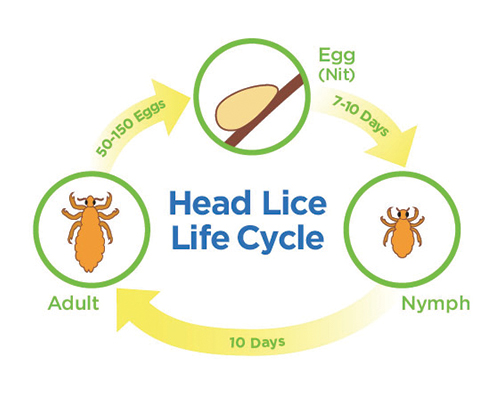
About the Nit, the Nymph and the Louse:
1. One nit can hatch after 8-12 days and then becomes a nymph (a young louse).
2. A female louse will become an adult in 3-5 days and lay 6 or more nits per day.
3. Lice can live about 30 days on your head in their lifetime – that can be a lot of eggs if left untreated.
Where Do Head Lice Come From?
1. Nobody is certain about the origin of head lice.
2. Head lice are everywhere and can even be dated back to mummies in ancient Egypt.
How Do Head Lice Stay on My Hair?
1. Lice have tiny but powerful claws that hold onto the hair.
Can You Get Lice from Your Pet?
1. No. Lice do NOT live on animals.
2. Pets do NOT play a role in the spread of head lice.
3. Head lice are HUMAN parasites and do not live on animals.
Q: What are some head lice symptoms?
You may have head lice and might not even know it. In many cases there are no symptoms at all, especially if it is your first time getting head lice. Most often though people feel a tickling sensation or something that feel like it is crawling. It just does not feel right. Like your scalp is moving. Another sensation is itchiness. This is an allergic reaction to the saliva from lice after they feed on blood from the scalp. Those are symptoms that are pretty common. It is best to look in the mirror or have someone look through your hair to see lice is present or to go to a professional treatment to see if you have a case of lice.
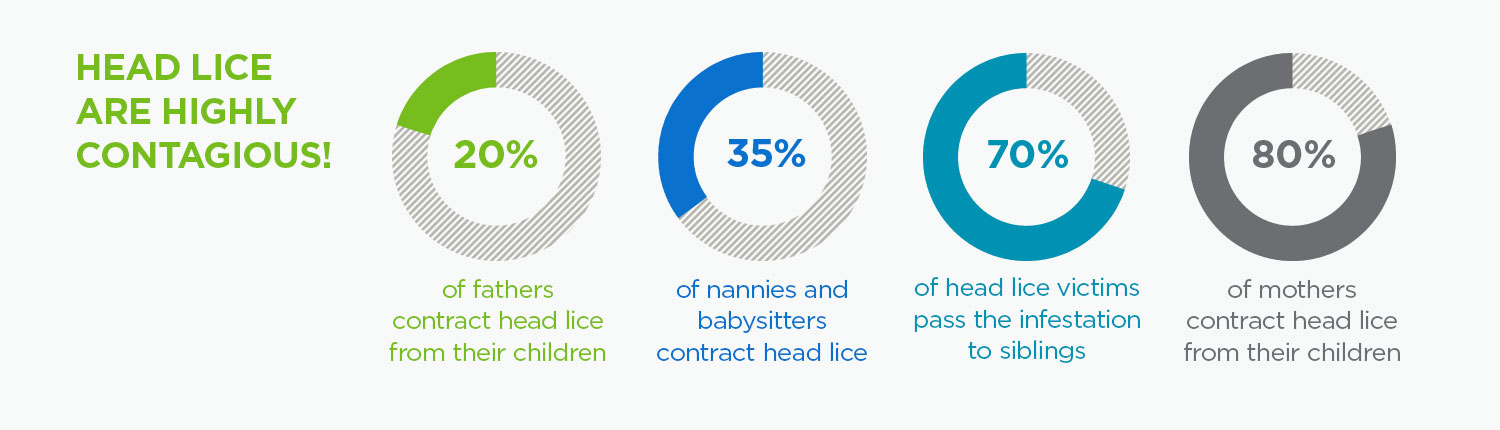
Because lice is spread through head-to-head contact, all immediate family members are at risk when a family member has lice. Half the people we treat are children under 18 but the other half are adults, usually moms. All lice need to survive is a hair strand and a warm scalp. So people with short hair (including dads) can and do get head lice.

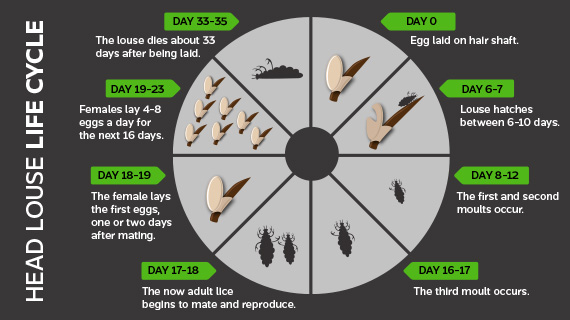
Human head lice don't live very long. Maybe about 30-45 days is their entire life cycle. They need human blood to survive. They feed about every 2-3 hours off the scalp of the head. If they come off the scalp, should that happen, they die within 24-48 hours. They don't like to come off the scalp. They need high heat and high humidity to survive. They like to lay their eggs on the hair shaft very close the scalp where it is nice and warm and nice and humid. When those eggs hatch, they can immediately get on the scalp and feed on the blood. Adult females lay 80 to 90 eggs during their lifetime and their eggs take about 8 to 9 days to hatch. Infestations will continue literally for years if you don't seek treatment so we recommend that you seek treatment and make sure you find out if you have a case of head lice or not.
Lice survive by sucking the human blood every two to three hours. Itching is an allergic reaction to the lice saliva. 40% of the people that have lice are allergic to the lice saliva and itch however 60% of the people that have lice don’t itch.

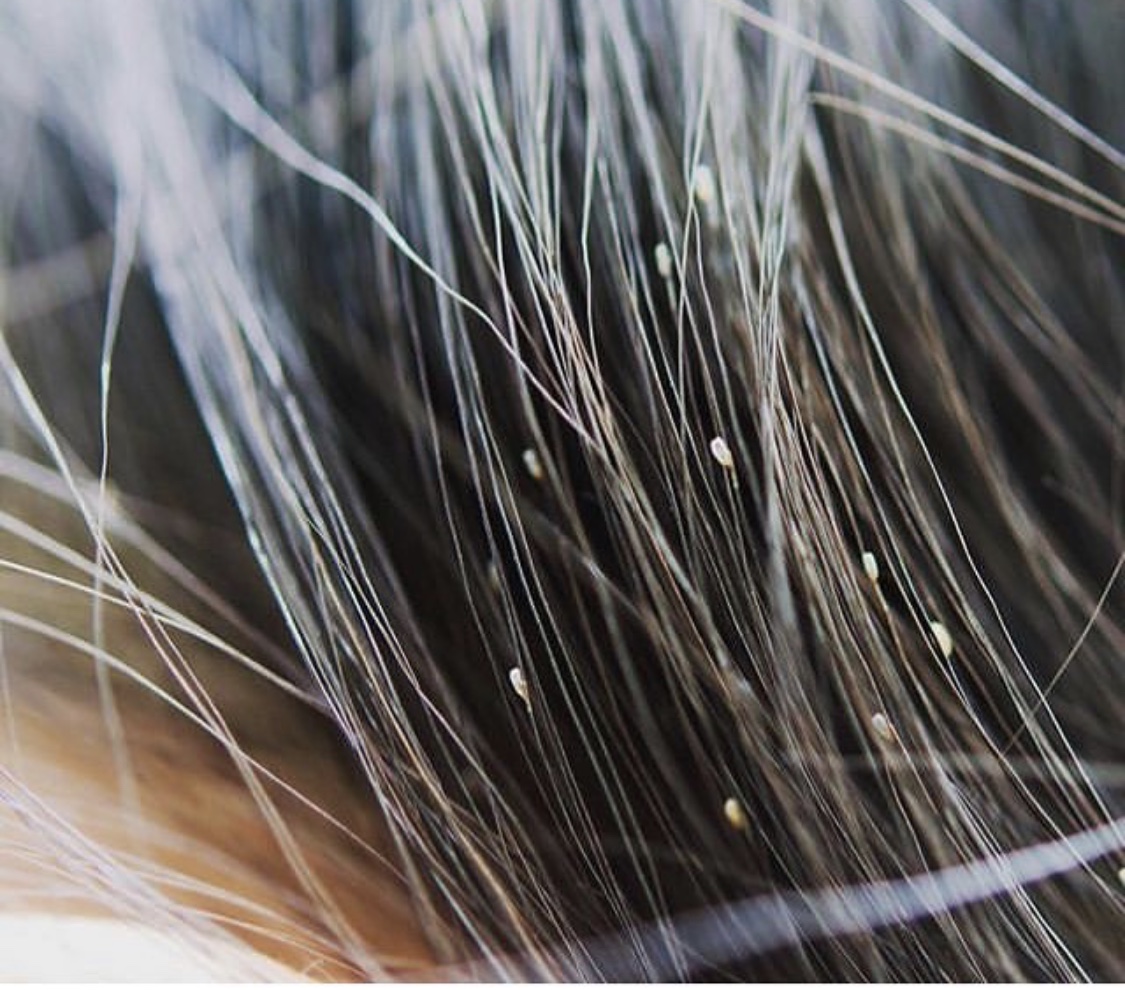
Lice live towards the nape of the neck and the back of the head so it is almost impossible to head screen and/or treat yourself.
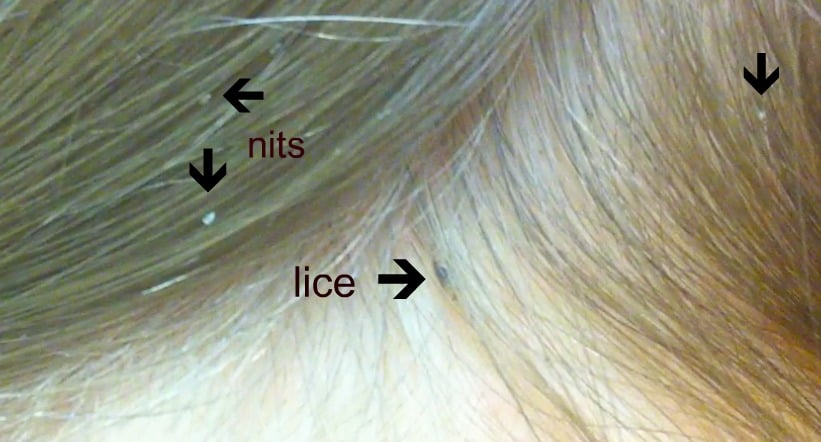
The biggest challenge in ending a lice infestation are the lice eggs. They are the size of a grain of sand and do not move. They are typically glued to the hair strand. They also have a protective shell that product simply cannot penetrate. Because they are not yet hatched, they do not suck blood or cause itching.
Most people head straight to the local drugstore and buy over-the-counter shampoos such as RID or NIX and apply the product to their child’s hair only to find that it does not work-the lice and their eggs are still there. The primary chemical in these products is Permethrin. The lice have mutated and now recognize this chemical. In addition to not ending the lice infestation, these products are full of chemicals that can also cause itching and irritation on the scalp.
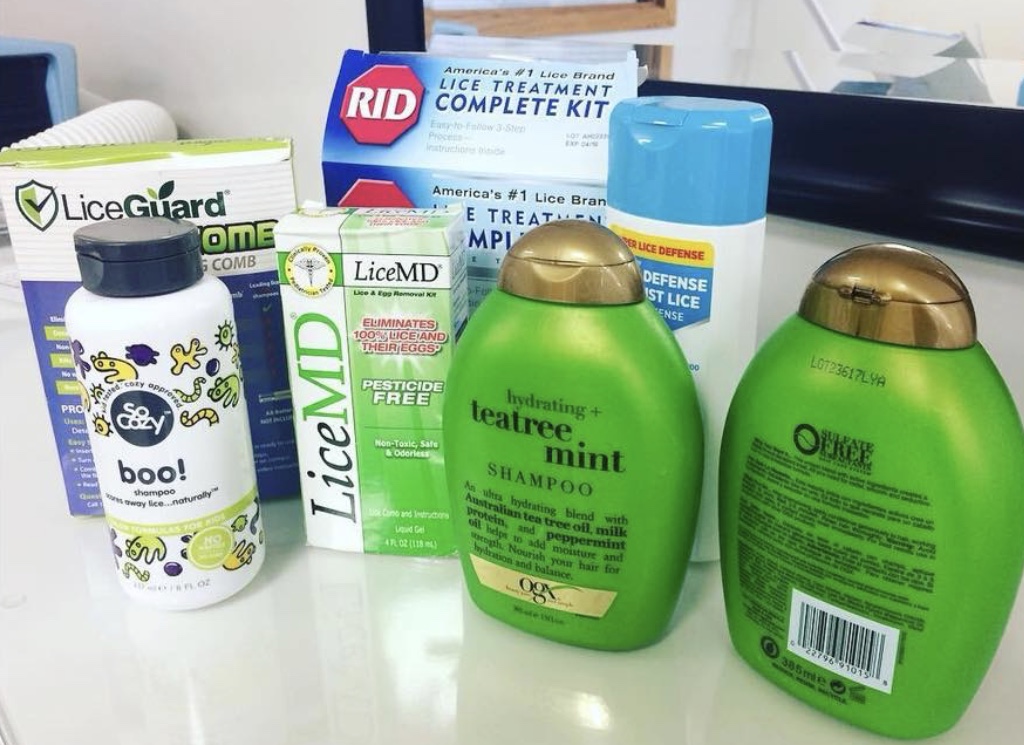



Traditional lice treatments require multiple applications and tedious nitpicking to remove eggs. Even worse, traditional drug store products no longer work because Super Lice are pesticide resistant. Lice have developed resistance to the pesticides the traditional products use, and it is not uncommon for families to struggle with head lice for weeks or months at a time trying to treat your head lice infestation yourself. It can also be a real challenge treating your own child and a strain on your relationship versus having a professional treat your child.

Savvy parents know that getting rid of the lice eggs is the biggest challenge of ending a head lice infestation. Lice eggs are glued to the hair strand, the size of a grain of sand, and don’t move.
Lice eggs have a protective shell that product simply cannot penetrate.


Lice do not care about age, income, ethnicity, time of the year, gender, if you have had lice before or not, or how long you have had lice. The cost of treating lice yourself can add up quickly in addition to being time consuming, stressful, and you can still have lice.
Due to the lice life cycle, you can soon have several hundred eggs in your hair and have lice for days, weeks, months, and even years. What’s more, 50% of the people we treat are children ages 3-17 but the other 50% are adults. Trying to treat yourself is almost impossible.
Many families come to us after they have unsuccessfully spent many long hours trying to treat it themselves with no results and lots of wasted time and money.
By that time, the infestation has become much worse and other family members and close friends have been infested since lice is spread through head-to-head contact.
If not treated properly, the head lice infestation does not just "go away." A person can have lice for days, weeks, months, or even years.
We have a comprehensive 100% chemical-free process, have a 99%+ success rate, a 30 day lice free guarantee,
We can get you lice free in about 1 hour.

TYPES
There are many types of lice, the head louse, or Pediculus humanus capitis, is a parasitic insect that can be found on the head and, more rarely, the eyebrows and eyelashes of people.
LIFE CYCLE
There are three stages of the lice life cycle: egg, nymph and adult.
ANATOMY
Head lice have six claws designed for them to crawl from hair strand to hair strand. These claws allow them to move from head to head.
HEAD TO HEAD
A head-lice infestation occurs when a female adult louse moves to a new head and lays eggs. When those eggs hatch, the lice will most likely stay on that head throughout the entire lice life cycle. Unless the head is treated and all lice and eggs are eradicated, the lice infestation will continue for however long the lice can live.

